In our modern diet, sugar plays a significant role, often appearing in many forms and sources. While it can be a quick source of energy and an enjoyable part of our meals, the amount and type of sugar we consume can profoundly impact our health.
Understanding the recommended daily intake of sugar, the best and worst sources, and the consequences of consuming too much or too little sugar is crucial for maintaining a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle. This article delves into these aspects, providing clear insights and practical advice on managing sugar consumption effectively.
How much sugar do we need per day?
The amount of sugar a person should consume per day varies based on health guidelines. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that free sugars should make up less than 10% of total daily energy intake, with a further reduction to below 5% providing additional health benefits.
For an average adult with a normal body mass index (BMI), this translates to:
- Less than 50 grams (about 12 teaspoons) of free sugars per day to stay below the 10% threshold.
- Less than 25 grams (about 6 teaspoons) of free sugars per day to stay below the 5% threshold for additional health benefits.
Free sugars include those added to foods and drinks as well as sugars naturally present in honey, syrups, fruit juices, and fruit juice concentrates.
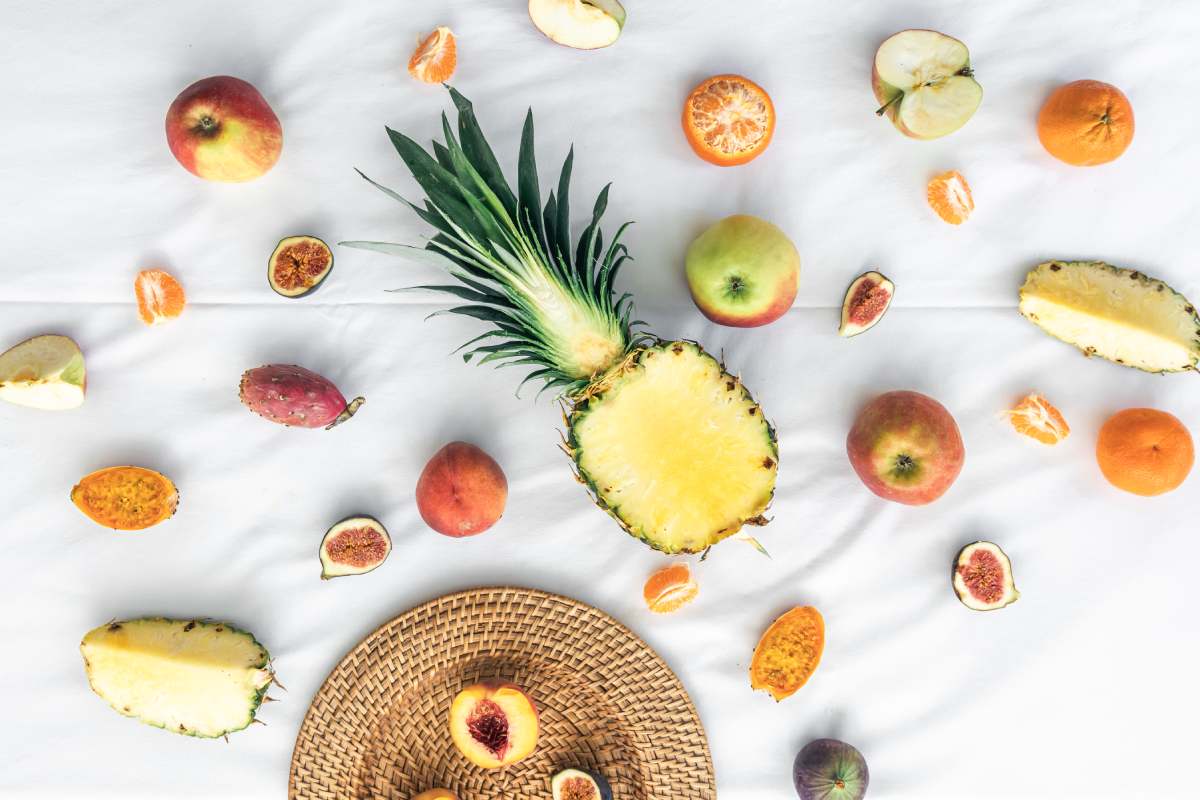

What are the best sources of sugar?
When considering sources of sugar, it’s important to differentiate between natural sugars found in whole foods and added sugars that are incorporated into processed foods and beverages. Here are some of the best sources of natural sugars:
- Fruits: Fruits are excellent sources of natural sugars along with vitamins B12, C and E, minerals, and fibre. Examples include apples, bananas, berries, oranges, and mangoes.
- Vegetables: Some vegetables contain natural sugars. These include sweet potatoes, beets, carrots, and corn.
- Dairy Products: Milk, yoghurt, and cheese contain lactose, a natural sugar. These also provide protein, calcium, and other essential nutrients.
- Whole Grains: Whole grains like oats and quinoa have natural sugars and are also high in fibre and other nutrients.
- Honey and Maple Syrup: While these are natural sweeteners, they should be used sparingly due to their high sugar content.
To manage sugar intake effectively, it’s generally better to focus on consuming whole foods and minimizing the intake of added sugars found in processed foods and sugary beverages.
What are the worst sources of sugar?
The worst sources of sugar are those that provide little to no nutritional value and can contribute to various health issues when consumed in excess. These include:
 Sugary Beverages: This category includes sodas, energy drinks, sweetened teas, and fruit punches. They often contain high amounts of added sugars and provide empty calories.
Sugary Beverages: This category includes sodas, energy drinks, sweetened teas, and fruit punches. They often contain high amounts of added sugars and provide empty calories.- Candy and Sweets: Items like candies, chocolates, gummy bears, and lollipops are high in added sugars and often lack essential nutrients.
- Baked Goods: Cakes, cookies, pastries, doughnuts, and muffins typically contain high amounts of added sugars and unhealthy fats.
- Ice Cream and Desserts: Ice creams, frozen yoghurt, puddings, and other desserts are often loaded with added sugars.
- Sweetened Breakfast Cereals: Many breakfast cereals marketed to children and adults contain significant amounts of added sugars.
- Processed Foods: Many processed foods like flavoured yoghurts, granola bars, and some types of bread and sauces (such as ketchup) contain hidden sugars.
- Fruit Juices and Smoothies: Even though they come from fruit, many commercially available juices and smoothies have added sugars and lack the fibre found in whole fruits.
Consuming these sources of sugar regularly can lead to various health issues such as weight gain, increased risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and dental problems. It’s advisable to read nutrition labels and be mindful of the sugar content in the foods and drinks you consume.
What happens if we consume too much or too little sugar?
Consuming Too Much Sugar:
- Weight Gain: Excessive sugar intake, especially from sugary drinks and snacks, leads to increased calorie consumption, which can result in weight gain and obesity.
- Increased Risk of Heart Disease: High sugar consumption is linked to higher risks of heart disease due to increased triglycerides, blood pressure, and inflammation.
- Type 2 Diabetes: A diet high in sugary foods and beverages can lead to insulin resistance, increasing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Dental Problems: Sugars feed the bacteria in the mouth, leading to plaque formation, tooth decay, and cavities.
- Liver Disease: Excessive intake of fructose (found in many sweetened beverages) can cause fatty liver disease.
- Poor Nutrition: High sugar consumption can displace healthier foods in the diet, leading to nutrient deficiencies.
- Increased Risk of Cancer: Some studies suggest that a high-sugar diet may increase the risk of certain cancers, though more research is needed.
- Skin Aging: Excess sugar can damage collagen and elastin in the skin, leading to premature ageing.

Consuming Too Little Sugar:
- Low Energy Levels: Sugar is a primary source of energy. Insufficient intake can lead to low energy levels and fatigue.
- Hypoglycemia: Very low sugar intake can cause hypoglycemia, characterized by symptoms like dizziness, shaking, sweating, confusion, and irritability.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Avoiding foods that contain natural sugars, such as fruits and vegetables, can result in a lack of essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and fibre.
- Mental Health Effects: Low blood sugar levels can impact mood, causing irritability, anxiety, and difficulty concentrating.
- Reduced Athletic Performance: Athletes and active individuals might experience reduced performance and endurance without adequate carbohydrate intake, including sugars.
Balance is key. Consuming natural sugars from whole foods while limiting added sugars from processed foods and beverages helps maintain overall health.
Final thought
You’ve got to balance your sugar intake for good health. Natural sugars from whole foods like fruits, veggies, and dairy give you important nutrients and energy. But eating too many added sugars from processed foods and drinks can cause problems like obesity, heart disease, and diabetes. On the flip side, not getting enough sugar can leave you feeling tired and lacking in nutrients.
If you make smart choices about the types and amounts of sugar you eat, you can have a well-rounded diet and avoid the downsides of bad eating habits. Just remember, it’s all about moderation and being mindful when it comes to sugar.
 Sugary Beverages: This category includes sodas, energy drinks, sweetened teas, and fruit punches. They often contain high amounts of added sugars and provide empty calories.
Sugary Beverages: This category includes sodas, energy drinks, sweetened teas, and fruit punches. They often contain high amounts of added sugars and provide empty calories.